World Economic Forum report discusses the Wild Wide Web
The 2020 edition of the WEF’s Global Risk Report discusses how emerging technologies, such as quantum computing, have the power to transform human lives; but also warns of the risks they pose to the global economy by making society more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
About the Global Risk Report 2020
Now in its 15th year, the report explores the biggest threats that society will face over the course of the year, and beyond. It was authored by the World Economic Forum, together with Marsh & McLennan and Zurich Insurance Group, as part of the Forum’s expanded Global Risks Initiative.
The overarching theme of this year’s report is that of ‘an unsettled world’; where “powerful economic, demographic and technological forces are shaping a new balance of power. The result is an unsettled geopolitical landscape – one in which states are increasingly viewing opportunities and challenges through unilateral lenses.”
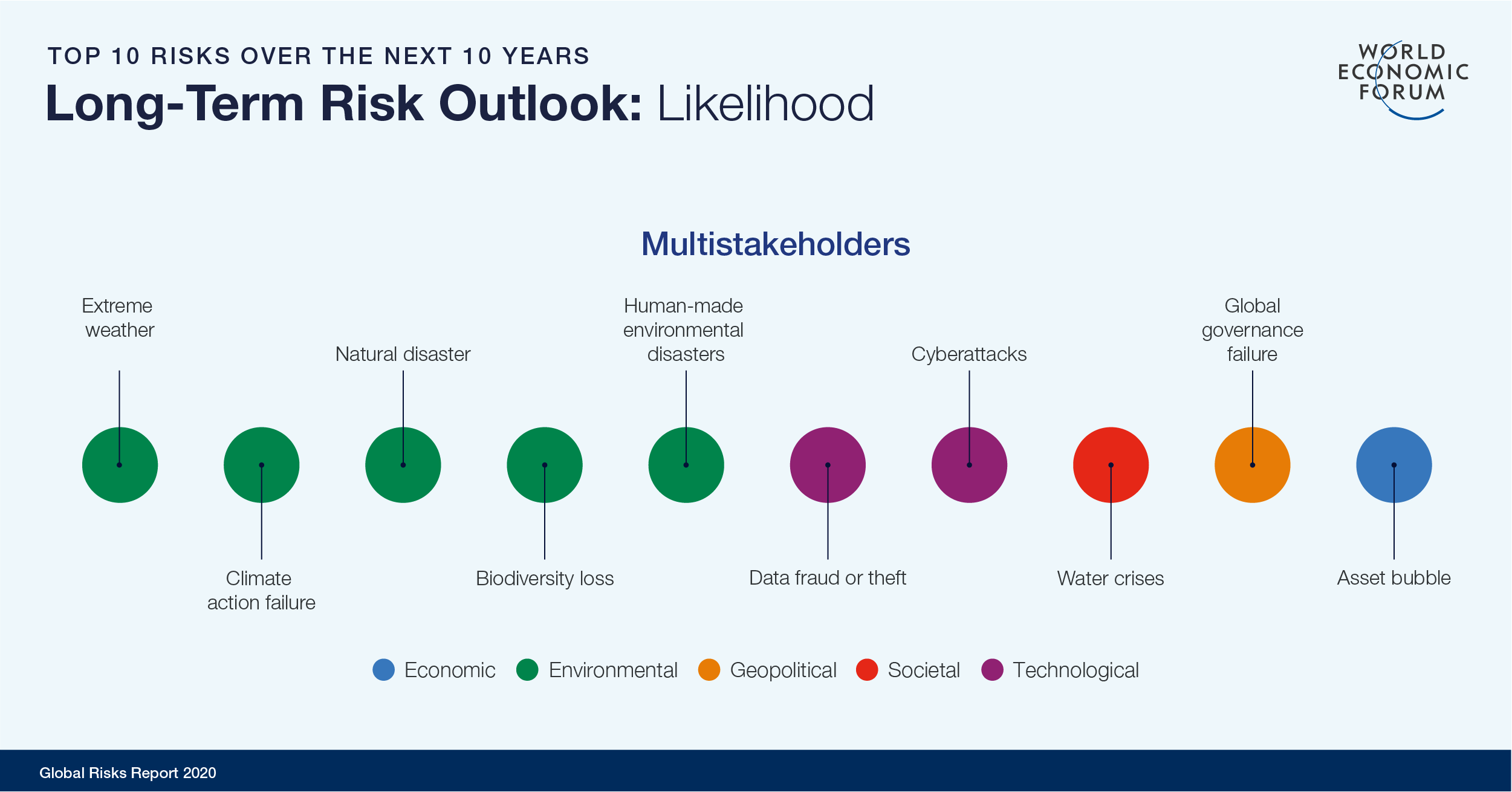
The report identifies five “global shapers” of the risk landscape: economic, environmental, geopolitical, societal and technological. In the wider context, it places these technological risks behind the five environmental challenges of extreme weather, climate action failure, natural disaster, biodiversity loss and man-made environmental disasters.
This is the first time that all five of the report’s top spots have been occupied by a single category, while technological risks remain firmly placed in the top 10.
The Wild Wide Web
Within a section aptly titled ‘Wild Wide Web’, the report discusses how lack of global technology governance and cybersecurity blind spots increase the risk of a “fragmented cyberspace” and competing regulations. It also mentions how these elements, together with other factors such as geopolitical tensions, can negatively influence the economic potential of next-gen technologies.
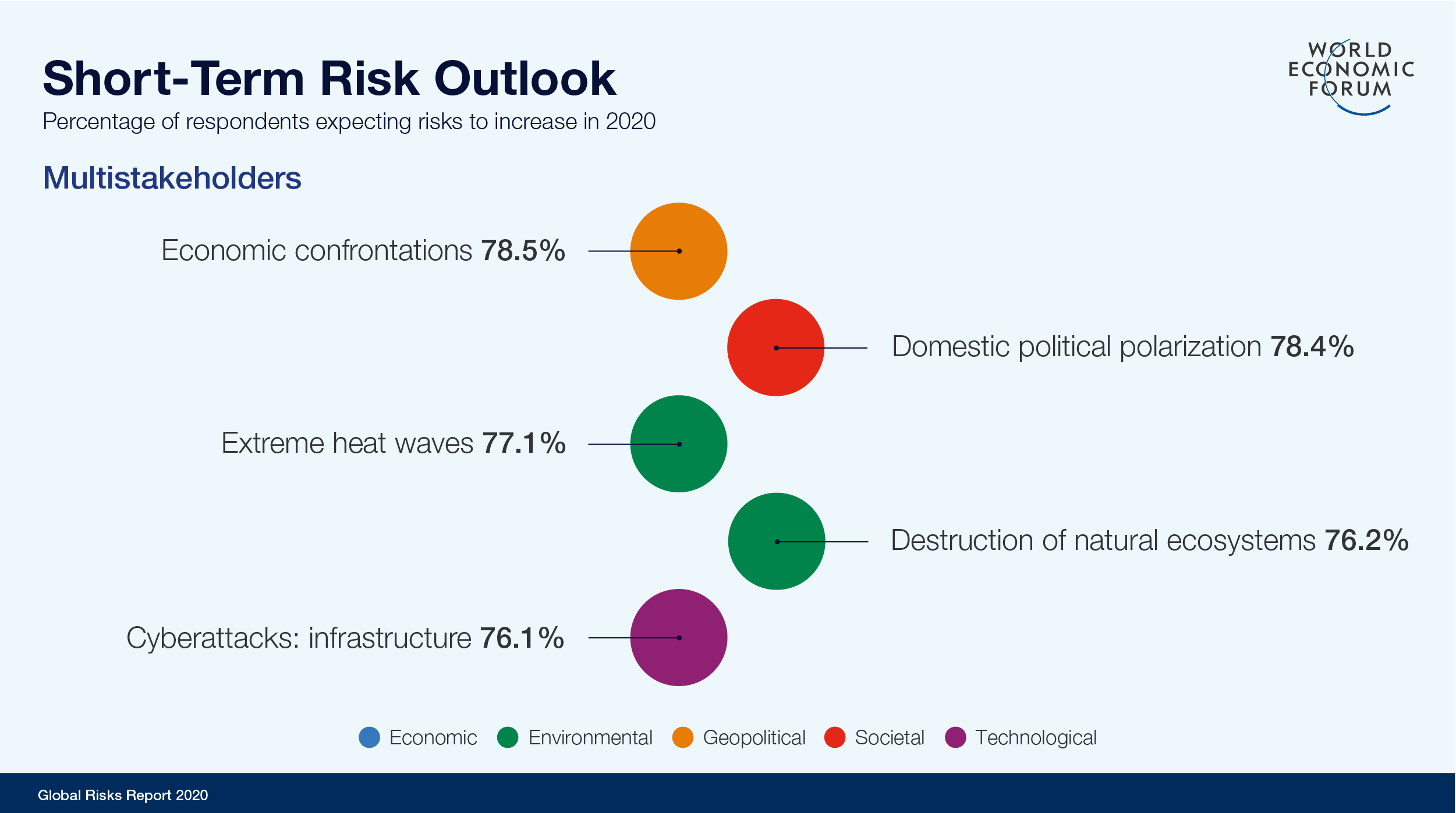
Data fraud or theft and cyberattacks both featured in the top 10 most likely global risks (sixth and seventh respectively), while information infrastructure joins cyberattacks in the top 10 most impactful risks (sixth and eighth respectively). Moreover, 76.1% of survey respondents expect the risks of cyberattacks to increase in 2020, making it the fifth top risk identified.
50%
of the world’s population is now online
The report also speaks about the fourth industrial revolution (4IR) and now emerging technologies could influence a world in which 50% of the population is now online. It states that “fifth generation (5G) networks, quantum computing and AI are creating not only opportunities but also new threats of their own.”
Expanding on this comment, the report goes on to explore the dangers of digital innovation. The vulnerability of 4IR technologies to cyberattacks, the risk of data theft, the influence of AI and cloud computing, and the rise of 5G and 6G technologies are all highlighted as areas where security and governance must be addressed.
The report also acknowledges the risks of quantum computing, stating that it “could dramatically reduce the time needed to solve the mathematical problems on which encryption techniques currently rely – from months to minutes and seconds. It risks rendering useless most of our existing data security and critical infrastructure systems, including military networks, email and power grids.”
ID Quantique at Davos
Grégoire Ribordy, CEO and co-founder of ID Quantique participated in a panel discussion on the topic of “Quantum Challenge for the future”. The acknowledgement of quantum computing as a risk that the world needs to address, together with its impact, shows that the technology has truly moved onto the global stage.
For some reading the report, it may seem that securing their organisation against the threats of quantum computing is not yet possible. However, this isn’t the case.
Quantum-safe security technologies, such as Quantum Random Number Generators (QRNGs) and Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) are already commercially available; exploiting unique properties of quantum physics to protect against cyberattacks from classical and quantum computers alike.
When evaluating their cybersecurity preparedness in the post-quantum world, organisations should get a head-start by implementing QRNG and QKD technologies today. This offers a quantum-safe solution that mitigates the risk of both classical and quantum attacks.

You can download the full WEF Global Risk Report 2020 here, or find out more about quantum-safe security.



